Supercritical CO2 Extraction of solid raw material
Extraction of solid raw materials with supercritical CO2 is the most common application of using the unique properties of CO2 at high pressures. It is used for separating soluble from insoluble components and can be applied on countless different materials.
For many applications CO2 has well-suited solvent properties which can be easily tuned by changing pressure and temperature. In addition, carbon dioxide in the supercritical state has a very low viscosity and no interfacial tension. Therefore, it can penetrate very well into the structures of solid raw materials. These properties make it suitable for many different processes.
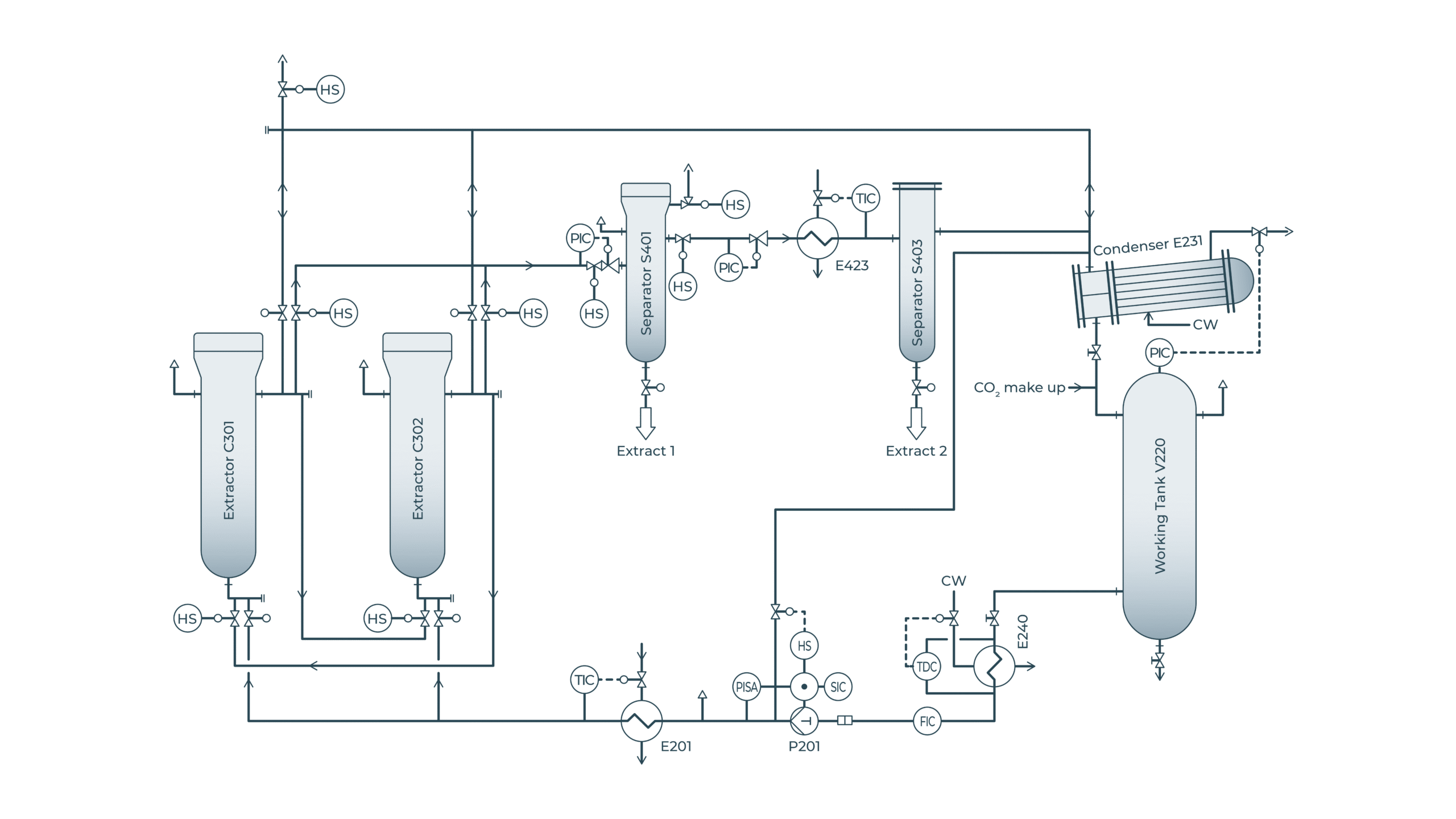
A typical supercritical CO2 extraction system is shown schematically in the picture above. The process starts at the working tank, where the CO2 is stored for the operation. It is then compressed in a high-pressure pump and brought to the desired extraction temperature. Afterwards it is directed into one of the extraction vessels in which the carrier material is located. The extractors are equipped with quick opening closures to allow easy and safe filling and discharging. Solid raw materials are typically fed into the extractor by means of a basket or directly into the vessels. Several extraction vessels can be combined to a functional system so that extraction can be carried out on a continuous basis despite the batch operation of the extractors.
This operation is commonly called semicontinuous and is about redirecting the flow between the extractors. After leaving the vessels the loaded carbon dioxide reaches the separators where the change in pressure and / or temperature causes the precipitation of the extract out of the carbon-dioxide flow. The extract is then collected at the bottom of the separators. By using two or more separators working at different pressure and temperature conditions it is possible to obtain CO2 with different solvent properties allowing fractionation of the extract into different separators. In the last separator the CO2 is expanded to a gas state to remove all the remaining compounds. This pressure level is of importance since energy intensive recompression should be avoided. After separation the gas is liquified in a condenser and fed back into the working tank and ready to be used again.
Why supercritical CO2 extraction
Industrial Applications
There is a long list of CO2 extraction plants or machines but not a clear definition on what the scale of an industrial plant is because this might be very different between the pharmaceutical industry and the conventional food industry. Here is a list of a few:
Extraction of Hops:
Hops is used worldwide by the brewing industry to bitter the beer. After harvesting, the hops must be immediately dried to reach better stability. Even then, the storage life of hops is relatively short. More than 30% of the world´s hop production is extracted to supply the brewing industries continuously. Until 1980, most extraction plants operated with polluting and harmful organic solvents such as methylene chloride. Only a minority used ethanol. Nearly all extraction plants in the US, Europe, and Australia switched to CO2 extraction since then. The worlds biggest plant for CO2 extraction of Hops was built and start up by Natex in 2021 in Germany. It processes around 10.000t of raw material per year.
Decaffeination of Coffee and Tea:
Decaffeination was one of the first processes which was industrialized based on a supercritical CO2 process. It utilizes CO2 and water to remove caffeine from the green coffee beans or from fermented tea. The process was realized for scales up to 10.000 tons per year and can be energetically optimized at industrial scale by using an isobaric process.
Extraction of spices & herbs:
Spices and herbs play an important role in our daily life and can be found in all types for food, beverages, washing agents or perfumes. Supercritical CO2 is a great solvent for concentrating the aromatics by extracting its essential oils and oleoresins from the raw material. In a lot of cases, plants are not fully dedicated to one specific product but used for a variety of different spices and herbs. This highlights the importance of easy cleaning and fast product changes. The biggest plants for extracting these types of raw materials are installed at their place of origin to avoid volumetric transportation, microbial contamination and increase the value created in the exporting country. Important spices for CO2 extraction are:
Cleaning of Cork:
Secondary metabolites produced by fungal or bacterial infections can damage cork quality. The most recognized one is 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole (TCA), which is responsible for the typical “cork taint” and causes drastic losses in the wine industry. Cleaning contaminated cork with supercritical CO2 is therefore used to remove the smelly TCA from otherwise good cork and allow the production of high quality technological cork stoppers. Natex is working on this topic since 2003 and built 3 big industrial plants with a capacity to clean approximately 4 billion cork stoppers per year.
Drying of Aerogels:
Aerogels have been known for decades and can be produced from inorganic materials like silica or metal oxides or from cellulosic materials. They belong to a group of materials with a high porous structure, a low solid content and a very low bulk density. They are known as the lightest solid material on earth and are mainly intended to be used as insulation material, whereas there are also several other applications. Due to its sensitive structure, supercritical CO2 extraction is the preferred way of drying it after it is produced and a solvent exchange has been executed.
Protein concentration / Defatting of press cakes:
Cold pressing of materials like Sunflower seeds, Rape seeds, Pumkin seeds, Hemp seed, Nuts and other is a well-established process in the food industry whereas this leaves a certain amount of lipids (6 – 12%) in the raw material which might get rancid over time and reduce the quality and possible applications of the residual protein. This remaining content can be easily removed by supercritical CO2 extraction to create a high quality protein source.
Our Expertise at NATEX Prozesstechnologie GesmbH
At NATEX Prozesstechnologie GesmbH, we possess extensive knowledge and experience in developing high-pressure extraction processes utilizing supercritical CO₂. Our capabilities include:
At NATEX Prozesstechnologie GesmbH, we are committed to advancing the CO2 extraction processes and providing our clients with innovative solutions backed by practical experience.